What Are Anal Warts?
Definition of Anal Warts
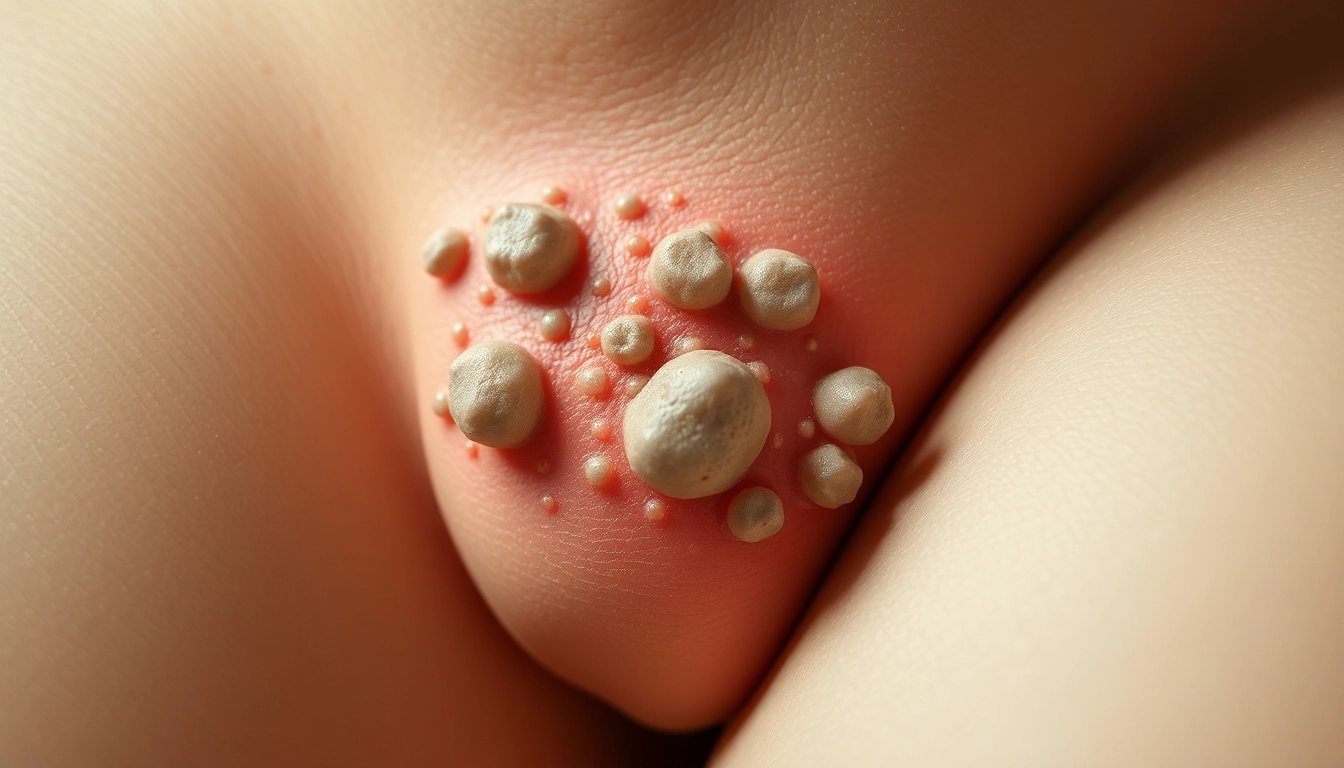
Anal warts, medically known as condyloma acuminata, are small, fleshy growths that appear around the anus and in the anal canal. They are a manifestation of infection by the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly the strains that are considered low-risk for causing cancer. The appearance of these warts can range from small, flat lesions to larger, raised growths that may have a cauliflower-like shape. Their prevalence can vary, but they are often associated with sexual activity due to the mode of transmission of HPV.
Symptoms Associated with Anal Warts
Individuals with anal warts may experience a variety of symptoms, although some may remain asymptomatic. Common symptoms include:
- Itching: A persistent itchiness around the anal region is a frequent complaint.
- Bleeding: Some individuals may experience discomfort or slight bleeding during bowel movements.
- Visible Growths: The presence of small, raised bumps around the anus, which might be mistaken for hemorrhoids.
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms arise, as they can be indicative of anal warts or other conditions, such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
Understanding HPV and Its Role in Anal Warts
The human papillomavirus is a large group of more than 150 related viruses, and it is among the most common sexually transmitted infections. While many strains of HPV are harmless and resolve on their own, others can lead to the development of anal warts. Transmission typically occurs through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. While the visible warts are generally not dangerous, certain strains of HPV are linked to higher risks of cervical cancer and other types of cancer, thus making regular medical check-ups crucial for sexually active individuals.
Causes of Anal Warts
How Anal Warts Are Transmitted
Anal warts are highly contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person. The primary mode of transmission is through direct contact with an infected area of skin. This can happen during sexual intercourse, but it can also occur through non-sexual skin-to-skin contact. Notably, even individuals who do not show visible warts can still transmit the virus, making it essential to practice safe sex and maintain open communication with partners regarding sexual health.
Risk Factors for Developing Anal Warts
Several factors can increase the likelihood of contracting anal warts, including:
- Engaging in Unprotected Sex: Those who do not use condoms are at a higher risk.
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple partners increases exposure to HPV.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to HPV and its effects.
- Younger Age: Adolescents and young adults are generally more prone to contracting sexually transmitted infections, including HPV.
Common Misconceptions About Anal Warts
There are several myths surrounding anal warts that contribute to misunderstandings about their nature:
- Only Sexually Active Individuals Get Anal Warts: While sexual activity significantly increases the risk, HPV can be contracted through non-sexual contact.
- Anal Warts Are Always Visible: Some individuals can carry the virus without displaying any symptoms or visible lesions.
- Warts Can Be Cured with Home Remedies Alone: While some home treatments may alleviate symptoms, professional medical intervention is often necessary for effective removal.
Diagnosis of Anal Warts
Diagnostic Procedures for Anal Warts
The diagnosis of anal warts is primarily made through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. During the examination, a doctor will look for signs of warts and may perform a visual inspection of the anal area. Additional tests, such as biopsies, may be conducted to rule out other conditions or complications associated with HPV. For accurate diagnosis, especially where lesions may be internal, a digital rectal exam may be performed.
Identifying Anal Warts vs. Other Conditions
It is essential to differentiate anal warts from other similar conditions. Conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and skin tags can present with similar symptoms. A trained professional can help distinguish between these conditions based on appearance, symptoms, and medical history. For example, hemorrhoids typically do not manifest as raised, fleshy growths, whereas anal warts are characteristically soft and can vary in size.
When to Consult a Professional
It is advisable to seek medical attention if you notice any unusual growths or persistent symptoms around the anal area. Additionally, anyone who has had unprotected sexual contact with someone diagnosed with HPV should also consult a healthcare provider, even in the absence of symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the symptoms and potential complications.
Treatment Options for Anal Warts
Topical Treatments for Anal Warts
Various topical treatments are available that a healthcare provider may recommend. These can include:
- Imiquimod Cream: This immune response modifier boosts the local immune system to help eradicate the warts.
- Podophyllin Resin: This topical medication is applied directly to the wart and works by destroying the wart tissue.
- Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA): This chemical agent is applied to the warts to cause localized cell death and can be effective for treatment.
It is essential to follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals regarding the application and frequency of these treatments for optimal results.
Procedures for Removal of Anal Warts
In situations where topical treatments are ineffective or if the warts are extensive, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common procedures include:
- Excision: Directly cutting out the warts.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrosurgery: Burning off the warts using an electric current.
Healthcare specialists often discuss the most suitable option based on the patient’s condition and overall health status.
Home Remedies and Preventative Measures
While professional treatment is essential, some individuals look toward home remedies to manage symptoms. However, it’s important to note that these remedies may not eliminate the virus but can provide relief. Common approaches include:
- Warm Baths: Soaking in warm water can relieve discomfort.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain.
- Proper Hygiene: Keeping the area clean and dry can help prevent irritation and secondary infections.
To prevent recurrence of anal warts, using protection during sexual activity, maintaining sexual monogamy, and considering the HPV vaccine can be beneficial.
Living with Anal Warts
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Anal Warts
Living with anal warts can lead to significant emotional distress for many individuals. Concerns about body image, sexual health, and the stigma associated with sexually transmitted infections can profoundly impact mental well-being. It is essential to approach this condition with understanding and seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or counseling services when needed. Discussing feelings and experiences can help alleviate anxiety and provide pathways to coping and recovery.
Preventing Recurrence of Anal Warts
While treatment can eliminate visible warts, there remains the potential for recurrence, especially if the underlying virus remains dormant in the body. To minimize the risk:
- Practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and correctly.
- Consider vaccination against HPV; vaccines are effective at preventing the most common cancer-causing and wart-causing strains.
- Maintain regular screenings with a healthcare provider to monitor and manage sexual health.
FAQs About Anal Warts
1. How long do anal warts last?
The duration varies significantly from person to person. Some individuals may experience warts that resolve on their own, while others may need treatment for persistent warts.
2. Can anal warts go away without treatment?
Yes, in some cases, the body’s immune system can clear the virus and the warts themselves, but medical intervention is often recommended for more severe cases.
3. Are anal warts contagious?
Yes, anal warts are contagious and can be easily transmitted through direct contact with infected skin.
4. Do anal warts indicate a serious health risk?
While anal warts themselves are usually not dangerous, they can indicate the presence of HPV, which carries a risk of certain cancers. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
In conclusion, understanding anal warts is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and effective treatment. If you suspect that you have anal warts or are experiencing related symptoms, seeking professional medical advice is important. For further information regarding Anal warts and managing your health, don’t hesitate to consult health resources or professionals.